|
Indian institutions offer a variety of technical undergraduate programmes in engineering, architecture, and planning via the Joint Entrance Examination - Main (JEE-Main), which was formerly known as the All India Engineering Entrance Examination (AIEEE). Admission to Bachelor of Technology (B.Tech) and Bachelor of Architecture (B.Arch) programmes at prestigious technical universities like NIT and IIIT is dependent on students' performance on the Joint Entrance Examination (JEE) Main. This test is administered by the National Testing Agency. Twice a year is the typical frequency.
The JEE Advanced exam for IIT's (Indian Institute of Technology) across India is the most difficult examination in the world followed by various other examinations such as Gaokao which is of similar level or on par with the JEE Advanced difficulty. Those who took the first session of the Joint Entrance Examination (JEE) Mains in 2024 may now see their results. These dates: January 24, 27, 29, 30, 31, and February 1 were the dates of the JEE Mains session 1 examinations. The official website now has the results and the final answer key, both of which were issued by NTA. Candidates are required to visit the official website in order to get the results. Two sessions will be held for the JEE (Mains) 2024. The JEE (Mains) 2024 first session results are out. The dates for the second session of the JEE Mains 2024 test are April 4–15, 2024. The second session of the Joint Entrance Examination (JEE) Mains registration period will end on March 2, 2024. More than 12 lakh individuals took the JEE Mains 2024. With seven pupils, Telangana has the largest number of students in the perfect percentile rank this year, which brings the total to almost twenty-three. After Telangana, three students each from Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, and Rajasthan achieved the 100 percentile. Only one student from each of the three states—Gujarat, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Delhi—scored in the top one hundredth percentile.
0 Comments
Temperatures on Earth have been 1.5 °C higher than pre-industrial levels for 12 months running, according to the European climate observatory. Experts in the field see this occurrence as a message to the human race. El Nino has exacerbated the world's already severe weather conditions, which include droughts, fires, and storms brought on by climate change.
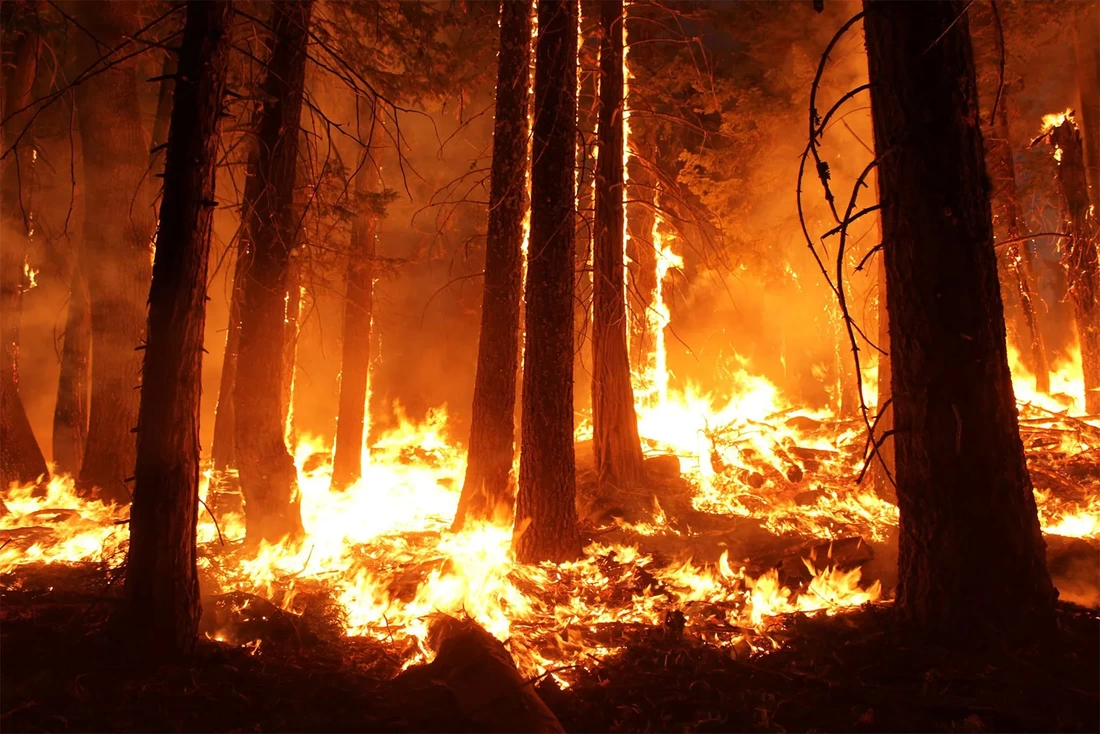
Due to this, 2023 is shaping up to be the warmest year in the past 100,000 years. The severe weather has continued into 2024, with the Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) revealing that temperatures were 1.52 degrees Celsius higher than the 19th-century average from February 2023 to January 2024. Even if this is a major indicator of the 1.5 degree Celsius critical warming barrier set by the Paris climate accord, it does not mean that the limit has been permanently violated. The limit is determined over decades, according to scientists. Heatwaves, droughts, floods, exacerbated storms, and water scarcity are just some of the prices that Johan Rockstrom from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research outlined while discussing the consequences of hitting 1.5 degrees Celsius. He stressed that the consequences of going beyond this limit were shown by what happened in 2023. A string of severe weather events have occurred around the world in recent months, including record-breaking rainfall in California, record-high winter temperatures in southern Europe, devastating wildfires in South America, and an Amazon basin drought. In light of recent events, Rockstrom has issued a stark warning that global warming is accelerating beyond the 1.5 degrees Celsius target set by the international community. Nevertheless, as El Nino passes, temperatures are predicted to drop slightly. Copernicus reports that January 2024 was the warmest on record, continuing a streak of eight consecutive months with record-high temperatures. Compared to the pre-industrial average for January between 1850 and 1900, the total temperature was 1.66 degrees Celsius higher. The combustion of fossil fuels is the main contributor to the ongoing increase in greenhouse gas emissions. In order to avoid going over the 1.5 degrees Celsius mark by the early 2030s, scientists stress the critical requirement of cutting these emissions in half within the next ten years. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) of the United Nations has issued a severe warning if this does not occur. "The Fiery Connection: Unraveling the Links Between Climate Change, Wildfires, and Public Health"11/11/2023 In recent years, the world has witnessed an alarming surge in the frequency and intensity of wildfires. This concerning trend is intricately tied to the impacts of climate change, posing not only environmental threats but also significant risks to public health. In this blog, we will explore the complex relationship between climate change, wildfires, and their repercussions on human health. Additionally, we will discuss proactive measures that can be taken to mitigate the increasing wildfire risks.
Rising Temperatures and Drought: One of the primary drivers behind the escalating wildfire crisis is the increase in global temperatures. As climate change leads to warmer and drier conditions, vegetation becomes more prone to ignition, setting the stage for more frequent and intense wildfires. Regions that historically experienced mild fire seasons are now grappling with prolonged and severe infernos. In 2019-2020 Australian bushfires, fueled by record-breaking temperatures and prolonged drought, devastated vast landscapes, resulting in loss of life, property, and biodiversity. Changing Rainfall Patterns: Climate change is altering precipitation patterns, contributing to prolonged periods of drought followed by intense rainfall. This erratic weather behavior exacerbates wildfire risks by creating conducive conditions for vegetation growth and subsequent ignition during dry periods. In 2020 California wildfires, exacerbated by a combination of prolonged drought and sporadic heavy rains, led to massive blazes that ravaged large areas and caused hazardous air quality. Air Quality Concerns: The smoke produced by wildfires contains a cocktail of pollutants, including particulate matter, carbon monoxide, and volatile organic compounds. Prolonged exposure to these pollutants poses severe health risks, especially to individuals with respiratory conditions, children, and the elderly. During the 2018 Camp Fire in California, residents experienced hazardous air quality levels, leading to an increase in respiratory issues and hospitalizations. Vector-Borne Diseases: Wildfires can alter ecosystems, influencing the distribution of disease-carrying vectors like ticks and mosquitoes. Changes in habitat and temperature can facilitate the spread of diseases such as Lyme disease and West Nile virus. The aftermath of the 2016 Fort McMurray wildfire in Canada saw an uptick in Lyme disease cases, attributed to changes in the behavior of tick vectors. Forest Management and Prescribed Burns: Implementing controlled or prescribed burns can help reduce fuel loads in forests, preventing the buildup of combustible materials. Proper forest management strategies, including thinning vegetation and creating firebreaks, can also limit the spread of wildfires. Australia has implemented controlled burning programs to reduce fuel loads, enhancing the resilience of ecosystems and minimizing the risk of catastrophic wildfires. Investing in Technology and Early Warning Systems: Utilizing advanced technologies such as satellite imagery, drones, and artificial intelligence can enhance early detection of wildfires. This enables swift response measures and aids in minimizing the extent of damage. In the United States, the use of the "Fireguard" system combines satellite data and weather forecasts to predict wildfire risks and support firefighting efforts. Community Education and Preparedness: Educating communities about wildfire risks and implementing preparedness measures, including evacuation plans and creating defensible spaces around properties, is crucial. Public awareness campaigns can help foster a proactive approach to wildfire prevention. In Sweden, community-based initiatives and education programs have played a key role in raising awareness and reducing the impact of wildfires. Addressing the interconnected challenges of climate change, wildfires, and public health requires a multi-faceted approach. By implementing proactive measures, investing in technology, and fostering community engagement, we can work towards building resilience against the growing threats posed by wildfires in a changing climate. It is a collective responsibility to protect our planet, mitigate climate change, and safeguard the well-being of present and future generations. The Beginning of a New Era in Brain Research: The Publication of the Most Detailed Map of the Brain10/26/2023 An international group of researchers has just released the most detailed map of the human brain ever made. This momentous accomplishment provides crucial groundwork for studying and treating brain-related illnesses and provides priceless insights into what makes us uniquely human.
Tomasz Nowakowski, a neuroscientist at the University of California, San Francisco and co-author of 21 papers in scholarly journals, said, "It's a dream that has been around for more than a century. This is like building a map of the universe. More than 250 academics from 45 institutions across three continents worked together for a decade on this ground-breaking study that cost the federal government over $500 million. Human brain tissue was used in the studies, either fresh from surgeries or preserved from postmortem donations. Thin sections of the living tissue were used to examine the properties of individual cells, while postmortem samples revealed information about the molecular composition of the brain's many specialized cell types. Over 3,000 distinct brain cell types were identified and their growth from infancy to adulthood was thoroughly tracked by the scientists. Creating a detailed map of the healthy human brain is the primary focus of this massive project. To better understand what goes wrong and where treatments might be targeted, this map will serve as a reference point for researchers examining a wide range of brain-related ailments. We had a map of the country, but the cities and streets were all blurry, and that's how it was with our understanding of the human brain until recently. Because of this murkiness, deciphering the mind's intricate workings was next to impossible. Similarities between the Human Genome Project, which released our genetic code in 2003 after more than a decade of labor and $2.7 billion in funding from the National Institutes of Health, and the brain-mapping program have been noted by researchers in the field of neuroscience. This ground-breaking feat paved the way for future developments in the biotech industry, such as consumer-facing genetic testing, diagnostic improvements for cancer and rare diseases, and forensic applications. As a result, groundbreaking initiatives such as the brain-mapping work detailed in these recent studies become possible. Some scientists believe that we have a better understanding of the solar system than of the complex neural networks in our brains, which they argue determine who we are and how we can do things like create music that moves us emotionally or perform difficult gymnastic feats. Alzheimer's disease, epilepsy, schizophrenia, autism, and depression are all brain-related illnesses, but the development of effective therapeutics has been hampered by the fact that much of what we know about brain anatomy and function has been gleaned from studying the brains of other animals. Because we don't fully understand what makes the human brain different from the brains of mice and nonhuman primates, promising medicines sometimes fail in animal testing. These new studies' ability to capture individual variances in human brains is groundbreaking. It's important to remember that the ratio of cells in critical brain regions is what truly sets humans apart from other mammals, not the sorts of cells themselves. For example, the findings reveal that glial cells, commonly referred to as "support" cells, in the human brain suffer more changes in gene expression than neurons, particularly when compared to the brains of nonhuman primates. This finding suggests that the substantial differences in our cognitive capacities as compared to other species may have their roots in quite tiny changes. Synapses are the building blocks of the brain's information processing and learning, and they are shaped in large part by glial cells. Furthermore, these investigations have revealed cell-level differences between different human brains. This fascinating discovery not only explains what it is that makes our brains human, but also highlights the ways in which each of us is special. The next step in the research process will involve characterizing the connections between brain cells rather than just researching the cells themselves. Deputy director of the National Institutes of Health's BRAIN Initiative Andrea C. Beckel-Mitchener views this partnership as "unprecedented in neuroscience." There has never been a more promising time to study the brain, with new avenues opening up that could lead to revolutionary new treatments for neurological disorders. In a remarkable feat of space exploration, NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission has returned to Earth with a monumental achievement— the largest asteroid sample ever collected. This momentous event marks a significant milestone in our quest to understand the origins of our solar system and life on Earth. The OSIRIS-REx mission, which stands for Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security, Regolith Explorer, was initiated by NASA in September 2016. The mission's objective was to study the asteroid Bennu, a carbon-rich celestial body with the potential to provide unique insights into the early solar system.
After a two-year journey through space, OSIRIS-REx reached Bennu in late 2018. Over the subsequent years, the spacecraft meticulously surveyed the asteroid, mapping its surface and characterizing its composition. The highlight of the mission, however, was the collection of a sample from Bennu's surface. This historic moment occurred in October 2020 when OSIRIS-REx descended to the asteroid's surface. The spacecraft's robotic arm, TAGSAM (Touch-And-Go Sample Acquisition Mechanism), briefly contacted Bennu, releasing a burst of nitrogen gas to stir up and collect regolith particles, including dust and pebbles. The TAGSAM's sampler head acted like a vacuum cleaner, efficiently collecting these precious pieces of the asteroid's surface. The collected sample was securely stored in a sample return capsule onboard the spacecraft. After a two-year journey through space, OSIRIS-REx successfully re-entered Earth's atmosphere, culminating in the safe return of the invaluable cargo. The significance of this mission lies in what these asteroid samples can reveal. Asteroids like Bennu are believed to contain materials that have remained relatively unchanged for billions of years, offering insights into the formation of our solar system and the origins of organic molecules, potentially shedding light on the building blocks of life. The OSIRIS-REx mission is not just an engineering marvel; it's a testament to the collaborative efforts of scientists, engineers, and space enthusiasts worldwide. It underscores our unwavering commitment to understanding the universe around us and the intriguing stories concealed within celestial bodies. As we eagerly anticipate the scientific discoveries that will emerge from this mission, it's a reminder of the boundless curiosity driving humanity's exploration of the cosmos. OSIRIS-REx's historic achievement is a triumph not only for NASA but for all those who ponder the mysteries of the universe when they gaze at the night sky. It reaffirms that the spirit of exploration is alive and well, and there are still numerous cosmic adventures awaiting us. In an awe-inspiring triumph of human exploration, NASA astronaut Frank Rubio has returned to Earth after an incredible 371 days in space, smashing the record for the longest spaceflight by an American. Rubio's journey concluded with a landing in Kazakhstan aboard a Russian spacecraft, marking the end of a historic mission.
It's good to be back, an undoubtedly relieved Rubio exclaimed as he was carried out of the spacecraft. His return was initially slated for March, but an unexpected encounter with a micrometeorite left his Russian-made return ship compromised and unsafe for travel, according to NASA. This unfortunate turn of events necessitated an additional six months aboard the International Space Station until a backup vessel was ready to bring him home. During a recent press briefing, Rubio candidly reflected on the roller coaster of emotions he experienced during his extended stay in space. He noted that had he known the true duration of the mission, he might have second-guessed his decision, as it meant missing pivotal family moments, such as sending his son off to college. Rubio and his wife are parents to four children. At the age of 47, Rubio embarked on an extraordinary journey back to Earth, landing in central Kazakhstan after a roughly four-hour descent. He made the journey alongside two cosmonauts from Roscosmos, the Russian Federal Space Agency, a testament to the enduring collaboration between U.S. and Russian space authorities, despite geopolitical tensions surrounding the conflict in Ukraine. Rubio's landing occurred at 7:17 a.m. Eastern time. Following their return, Rubio and his fellow cosmonauts were scheduled to be flown to eastern Kazakhstan, from where Rubio would board a NASA plane bound for Houston, home to the NASA Johnson Space Center. Rubio had already made history earlier in the month by surpassing the previous record for the longest spaceflight by an American, which was set at 355 days by astronaut Mark Vande Hei, according to NASA. This mission marked Rubio's inaugural journey into space. As a former U.S. Army surgeon and helicopter pilot, he joined NASA as part of the agency's 2017 astronaut candidate class. Rubio hails from Miami. Rubio anticipated feeling unwell during his initial hours back on Earth as his body readjusted to gravity. He shared that, like many returning astronauts, he would rely on medication and bags to ease the transition before getting some much-needed rest. Once he feels more like himself, Rubio expressed his eagerness to reunite with his wife and children, who displayed remarkable resilience throughout his unexpectedly lengthy stay in space. The return to terrestrial life may take a couple of months for him to regain strength and reacclimate to standing and walking. NASA Administrator Bill Nelson applauded Rubio's record-breaking achievement as a substantial contribution to our understanding of long-duration space missions. Rubio's mission, known as Expedition 68, focused on the impact of spaceflight on heart health and even included an intriguing experiment involving the growth of red dwarf tomatoes in space. This experiment aimed to test the feasibility of cultivating plants on future missions to the moon and Mars. Rubio shared his anticipation of reveling in the serene silence of his backyard after more than a year of enduring the constant hum of machinery aboard the International Space Station. He described his 371 days in space as an incredible personal and professional challenge, as well as an immensely rewarding experience. In healthcare and medical study, it doesn't happen very often that one drug changes the way people with more than one condition are treated. However, the weight-loss drug Wegovy has recently gotten a lot of attention, both for how well it fights obesity and for how it might help treat heart failure. Like any other medical advance, there are pros and cons to think about.
Pros of Wegovy: Weight-Loss Revolution It has been shown that Wegovy (semaglutide) can help people lose weight. This drug might help people lose weight, which is very important for public health. Lowering the risk of heart disease and stroke: In recent studies, wegovy lowered the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Because heart disease is so common around the world, this result is very important. Heart Failure Treatment: Along with weight loss, Wegovy may also help heart failure. Millions of people around the world are affected by this problem, and a drug that treats both obesity and heart failure could completely change the way cardiovascular treatment is done. Better Control of Blood Sugar: Semaglutide, which is a GLP-1 receptor agonist, helps people with type 2 diabetes better control their blood sugar. People with diabetes and obesity may gain from this double action. Wegovy's Bad Points It has side effects just like any other drug. People have said they felt sick and had diarrhea. Bad impacts are very important, especially for people who have stomach problems. Pricey: GLP-1 receptor drugs cost a lot of money. Wegovy might not be available to people who don't have full insurance or who live in countries where drugs are expensive. Long-Term Safety: Early clinical studies show good results, but more research needs to be done on long-term safety and side effects. As with any new medicine, it could take years for the full benefits to show up. You still need to make changes to your lifestyle; Wegovy is not a cure-all. To lose weight, you have to change what you eat and how much you exercise. Wegovy's possibility as both a weight-loss drug and a possible heart failure treatment is a big step forward in medicine. But it's important to carefully weigh the pros and cons. There are a lot of exciting opportunities with the drug's ability to help people lose weight and keep their hearts healthy, but possible side effects and costs should not be ignored. As with any medical treatment, it's important to talk to doctors and nurses to make sure that Wegovy is the right choice for each patient. More study is being done to find out if the drug is safe and useful in the long term for treating obesity and heart failure. Elephants have always been celebrated for their remarkable intelligence and social intricacies, but it's their iconic trunks that truly set them apart in the animal kingdom. Recent scientific research has uncovered intriguing insights into how the brain of these gentle giants plays a pivotal role in controlling their dexterous trunks, shedding light on the profound connection between these two remarkable features.
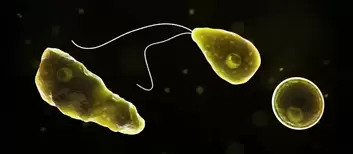
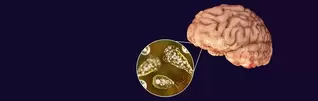
Elephants possess some of the largest brains in the animal kingdom, and a substantial portion of their cognitive prowess is devoted to the control and coordination of their trunks. What's even more astonishing is the sheer number of muscles within an elephant's trunk—approximately 150,000 individual muscle units. This level of muscular complexity allows them to perform an astounding array of tasks, ranging from delicate grasping to powerful digging. Modern scientific techniques, including advanced brain imaging, have enabled researchers to delve into the neural intricacies of elephant trunk control. Through these studies, they've pinpointed the specific regions of the elephant brain responsible for the intricate movements and actions of their trunks. Elephants appear to have a distinct "trunk area" in their brains, similar to the motor cortex in the human brain. This particular region is in charge of arranging their trunks' complicated and flexible movements. Surprisingly, researchers have noticed increased activity in this area when elephants do complicated tasks with their trunks, such as painting or manipulating things. The study also reveals the tremendous learning and adaptability built into the elephant's cognitive powers. Elephants perfect their trunk control over time, adjusting to diverse jobs as needed. This versatility is critical to their survival since they use their trunks for a variety of activities such as feeding, communication, social interactions, and even self-defense. Understanding the delicate link between an elephant's brain and trunk has far-reaching implications. This information has far-reaching ramifications for elephant conservation efforts. As we obtain a better understanding of these amazing creatures' cognitive and physical capacities, we will be able to devise more effective tactics for their preservation and well-being. The link between an elephant's brain and its extraordinarily dexterous trunk demonstrates the many complexity of these incredible animals. It emphasizes the critical necessity to safeguard and preserve both their physical and cognitive capacities. We can safeguard elephants' survival in the wild by solving the riddles of their intellect and adaptability, ensuring a brighter future for these majestic beasts for future generations. In the realm of medical diagnostics, speed and precision are paramount, especially when dealing with elusive and deadly pathogens. One such pathogen is the brain-eating amoeba, Naegleria fowleri. Its rapid diagnosis can be a matter of life and death, and traditional methods have often fallen short. Traditional Diagnostic Difficulties In the past, diagnosing brain-eating amoeba infections required invasive techniques such as cerebrospinal fluid tests and brain tissue biopsy. These approaches were not only time-consuming, but also dangerous. A Innovative Technology Meet metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS), a technology with the potential to change disease detection forever. It enables the quick and precise detection of infections, including the elusive brain-eating amoeba. How Does mNGS Work? Sample Collection: A sample of cerebrospinal fluid, blood, or tissue is obtained from the patient. DNA Sequencing: The genetic material in the sample, including the amoeba's DNA, is removed and sequenced. Bioinformatics Analysis: Advanced algorithms examine genetic data to identify possible infections quickly. Rapid Diagnosis: Results are available within hours, allowing for immediate treatment. The Potential of mNGS Comprehensive Pathogen Detection: A significant feature of mNGS is its ability to detect unexpected or unknown infections. Speed and precision: mNGS produces results in hours, whereas standard procedures take days or weeks. Non-invasive: It does not require intrusive procedures, which reduces patient discomfort and danger. While mNGS presents immense promise, it has its challenges, including cost and accessibility. As technology advances, we can expect this game-changing diagnostic tool to become more widely available and cost-effective, transforming the way we diagnose and treat infectious diseases. Metagenomic next-generation sequencing is a beacon of hope in the world of medical diagnostics. Its ability to swiftly and accurately detect even the most elusive pathogens offers a lifeline for patients facing infections like the brain-eating amoeba. As this technology becomes more accessible, it has the potential to save lives and make our world a safer place. CC:Articles and WSJ The deep ocean has long been regarded one of Earth's last frontiers, undiscovered and full of mystery. Interest in deep-sea floor mining for precious materials has developed dramatically in recent years. This activity may harm the ecosystem. An unexpected research mission in an area targeted by deep-sea miners found a plethora of wildlife, emphasizing the need to preserve this unique ecosystem.
In a groundbreaking research expedition, marine scientists explored a region of the deep ocean, previously earmarked for mineral extraction, and made a remarkable discovery. They identified and documented thousands of new species, shedding light on the incredible biodiversity that thrives in the abyssal depths. This discovery challenges our understanding of the deep sea and underscores the urgency of responsible environmental stewardship. The deep ocean, characterized by extreme pressure, cold temperatures, and perpetual darkness, is a challenging environment for life to thrive. Yet, life persists, and in the area targeted for mining, it thrives. The research team found an astonishing variety of species, from bioluminescent creatures that light up the darkness to strange and beautiful organisms adapted to the extreme conditions. Bioluminescent Wonders: Many deep-sea life forms survive on bioluminescence. They use their own light to attract prey or communicate in pitch-black conditions. New species include jellyfish, fish, and tiny crustaceans that use this remarkable adaption. Extraordinary Adaptations: Deep ocean inhabitants have adjusted to challenging environments. Some animals can tolerate crushing pressure, while others have advanced feeding apparatus for nighttime prey capture. Ecosystem Complexity: The study revealed this ecosystem's intricate species interactions. The deep-sea ecosystem's predatory connections, symbiotic partnerships, and complex food webs show the fragility of its millions-year balance. The revelation of such rich biodiversity in the area targeted by deep-sea miners has significant environmental implications. Mining activities in the deep sea could have catastrophic consequences for these fragile ecosystems. Here are some of the key concerns: Destruction of habitat: Mining harms the seabed, which could wipe out the homes of these newly found species and possibly cause them to go extinct. Pollution from chemicals: When minerals are taken from the ocean bottom, toxic chemicals and heavy metals may be released into the water. This could further upset the delicate balance of this ecosystem. Food Chains Could Get Messed Up: The complex food webs in the deep sea could get messed up, which would have effects all over the environment. The discovery of thousands of new species in the targeted mining area underscores the importance of responsible environmental stewardship. Here are some actions that should be considered: Protected Areas: Set up protected areas in the deep sea to keep mining and other activities that could harm these unique ecosystems from happening. Encourage the development of mining methods that are good for the environment, have a low effect, and put conservation first. International Cooperation: Work together on international deals and rules to govern deep-sea mining and protect biodiversity. The recent finding of thousands of new species in a location sought by deep-sea miners is proof of the deep ocean's treasures. It is also a sad reminder of our responsibility to maintain and preserve these vulnerable ecosystems. As we explore further into the sea in pursuit of precious resources, we must do so with the utmost care and regard for the extraordinary life forms that call the abyss home. Only by practicing appropriate environmental stewardship will future generations be able to marvel at the secrets of the deep sea. CC:WSJ and Mining articles |
|